Goiter Ayurvedic Treatment: Natural Remedies for Thyroid Health
Goiter Ayurvedic Treatment: Natural Remedies for Thyroid Health is a condition characterized by an abnormal enlargement of the thyroid gland, which is located at the base of the neck. It can occur due to various factors, such as iodine deficiency, autoimmune disorders, hormonal imbalances, or even environmental and genetic influences. In Ayurveda, the holistic system of medicine originating from India, the treatment of goiter focuses on balancing the body’s energy and restoring harmony between the mind, body, and spirit. This blog will explore the Ayurvedic approach to goiter, including natural remedies, dietary changes, and lifestyle modifications that can help manage this condition.
What is Goiter?
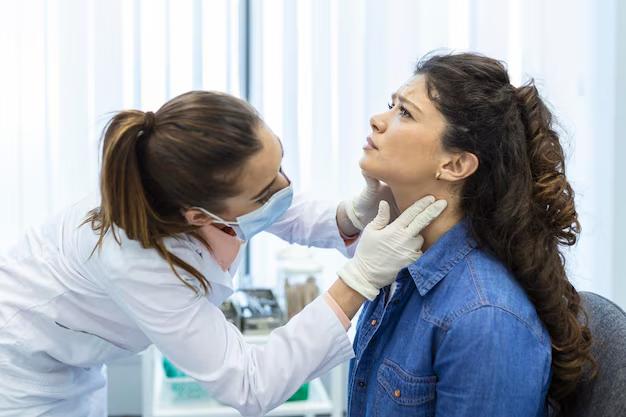
Before diving into Ayurvedic treatment options, it’s important to understand what goiter is and how it affects the body.
Goiter refers to the swelling or enlargement of the thyroid gland. The thyroid is responsible for producing hormones that regulate metabolism, energy production, and many other critical functions in the body. When the thyroid becomes enlarged, it can lead to both hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) or hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid), depending on the underlying cause.
Goiter can be classified into two main types:
- Diffuse Goiter: The entire thyroid gland is uniformly enlarged.
- Nodular Goiter: Lumps or nodules form within the thyroid, leading to an uneven enlargement.
Common causes of goiter include:
- Iodine deficiency: Iodine is essential for thyroid hormone production, and a deficiency can lead to goiter.
- Autoimmune diseases: Conditions like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (which leads to hypothyroidism) or Graves’ disease (which leads to hyperthyroidism).
- Thyroid cancer: Though less common, cancerous growths in the thyroid gland can cause goiter.
- Hormonal imbalances: Pregnancy, puberty, or menopause can affect thyroid function.
- Environmental factors: Exposure to certain toxins or heavy metals can influence thyroid health.
Ayurvedic Perspective on Goiter
In Ayurveda, the body is seen as an intricate system of energies, and any imbalance in these energies (Vata, Pitta, and Kapha) can manifest as physical symptoms or diseases. The thyroid gland, which regulates metabolism and energy production, is considered an essential organ in Ayurveda. When imbalances in the body’s doshas (energetic forces) occur, it can lead to thyroid disorders such as goiter.
- Kapha Dosha: The thyroid is mainly governed by Kapha, which is responsible for structure, stability, and growth in the body. An imbalance in Kapha dosha can cause the thyroid to become enlarged and sluggish, leading to goiter and hypothyroidism.
- Pitta Dosha: When Pitta (the fire element) is out of balance, it can lead to excessive heat in the body, resulting in hyperthyroidism or conditions such as Graves’ disease.
- Vata Dosha: Vata governs the movement and circulation of energy in the body. When Vata is imbalanced, it may lead to an irregular functioning of the thyroid gland.
Ayurvedic Treatment for Goiter
Ayurveda does not treat goiter as a condition isolated from the rest of the body. Rather, it looks at the individual holistically, considering their physical, mental, and emotional health. Treatment strategies aim to correct the root cause of the imbalance and restore equilibrium to the thyroid.
1. Herbal Remedies for Goiter
Ayurvedic herbs are a key component in the treatment of goiter. These herbs help to detoxify the body, reduce inflammation, and restore thyroid health. Some of the most commonly used herbs for managing goiter include:
- Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera): Ashwagandha is one of the most powerful adaptogens used in Ayurveda. It is believed to help regulate thyroid function and support the immune system. It can help balance both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism. Ashwagandha is commonly used in goiter management due to its ability to nourish the thyroid and reduce stress, which is often a contributing factor to thyroid imbalances.
- Kanchanar Guggulu: This is a traditional Ayurvedic formulation made from the Kanchanar herb (Bauhinia variegata) and Guggulu (Commiphora wightii). Kanchanar Guggulu has been used for centuries to treat goiter and other thyroid disorders. It is believed to reduce swelling in the thyroid and promote proper functioning of the gland. It is particularly effective in cases of benign goiter or nodular goiter.
- Guggulu (Commiphora wightii): Guggulu is another herb commonly used in Ayurvedic medicine for its anti-inflammatory and detoxifying properties. It helps to cleanse the body of toxins and supports healthy metabolism. Guggulu is also believed to help regulate the thyroid and promote its normal functioning.
- Brahmi (Bacopa monnieri): Brahmi is an adaptogenic herb known for its calming effects on the nervous system. It is often used to treat conditions like anxiety, which can aggravate thyroid imbalances. Brahmi can help reduce stress and inflammation in the thyroid, contributing to improved thyroid function.
- Guduchi (Tinospora cordifolia): Guduchi is another herb used to boost the immune system and detoxify the body. It has anti-inflammatory properties and is used to treat various thyroid-related issues, including goiter.
2. Dietary Changes
Diet plays a crucial role in managing thyroid health, and Ayurvedic principles emphasize the importance of nourishing the body with fresh, whole foods. For goiter management, the following dietary recommendations are often suggested:
- Iodine-Rich Foods: Iodine deficiency is one of the most common causes of goiter, especially in areas where iodine levels in the soil are low. To help restore iodine levels, include iodine-rich foods in your diet, such as seaweed (nori, kelp), iodized salt, dairy products, and fish. In Ayurveda, sea vegetables like kelp are highly recommended for balancing thyroid health.
- Anti-inflammatory Foods: Since goiter often involves inflammation of the thyroid gland, consuming anti-inflammatory foods can help manage the condition. These include turmeric, ginger, garlic, and green leafy vegetables. Anti-inflammatory spices such as cumin, coriander, and fennel are also beneficial.
- Avoid Goitrogenic Foods: Goitrogens are substances that interfere with iodine uptake in the thyroid and may worsen goiter. Common goitrogenic foods include cruciferous vegetables like broccoli, cauliflower, cabbage, and kale. Cooking these vegetables can reduce their goitrogenic effects, but it is best to consume them in moderation if you are dealing with goiter.
- Warm and Light Meals: Ayurveda recommends eating warm, freshly prepared meals that are easy to digest. Foods that are excessively cold or heavy can disrupt digestion and aggravate Kapha dosha, which can worsen thyroid imbalances. Opt for soups, stews, and cooked vegetables rather than raw salads.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of warm water throughout the day to aid digestion and help detoxify the body. Herbal teas made from ginger, turmeric, and holy basil (Tulsi) are excellent choices for improving circulation and reducing inflammation.
3. Lifestyle Modifications
In addition to herbal remedies and dietary changes, lifestyle plays a significant role in managing goiter. Ayurvedic lifestyle practices focus on balancing the doshas, supporting overall health, and preventing the recurrence of thyroid imbalances.
- Stress Management: Stress is one of the leading contributors to thyroid imbalances, including goiter. Practicing relaxation techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, or yoga can help reduce stress levels and promote a sense of calm. Yoga poses like the shoulder stand (Sarvangasana) and plow pose (Halasana) are particularly beneficial for stimulating the thyroid gland.
- Adequate Sleep: Ayurvedic texts emphasize the importance of sleep for overall health. Insufficient or poor-quality sleep can disrupt the body’s natural rhythms and lead to hormonal imbalances. Aim for 7-8 hours of restful sleep each night to allow the body to repair and rejuvenate.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can help stimulate thyroid function and improve metabolism. Gentle exercises such as walking, swimming, or yoga are recommended to avoid overstressing the body.
- Detoxification: Ayurveda recommends regular detoxification (Panchakarma) to remove accumulated toxins (ama) from the body. A detox program can help rejuvenate the thyroid gland and improve overall health. However, detoxification should be done under the guidance of a qualified Ayurvedic practitioner.
Conclusion
Goiter, while a potentially serious condition, can be effectively managed through Ayurveda by addressing the root causes of thyroid imbalance and supporting overall health. Ayurvedic herbs, dietary changes, and lifestyle modifications can help restore thyroid function and reduce the size of the goiter. As with any medical condition, it is essential to consult with a qualified Ayurvedic practitioner before starting any treatment, particularly if you are already on medication or undergoing conventional treatment for thyroid disorders. By adopting a holistic approach to health, you can support your thyroid and overall well-being naturally and effectively.

Leave a reply