Understanding Aortic Aneurysm and Ayurvedic Approaches to Management
Introduction
Understanding Aortic Aneurysm and Ayurvedic Approaches to Management is a serious medical condition characterized by the abnormal dilation of the aorta, the largest artery in the body. This condition can lead to life-threatening complications, including rupture and internal bleeding. While modern medicine offers various treatment options, many individuals seek complementary approaches to manage their health. Ayurveda, the ancient system of medicine from India, offers insights that may support overall cardiovascular health. This blog will explore the nature of aortic aneurysms, their symptoms, causes, and how Ayurvedic principles can be integrated into management strategies.
What is an Aortic Aneurysm?
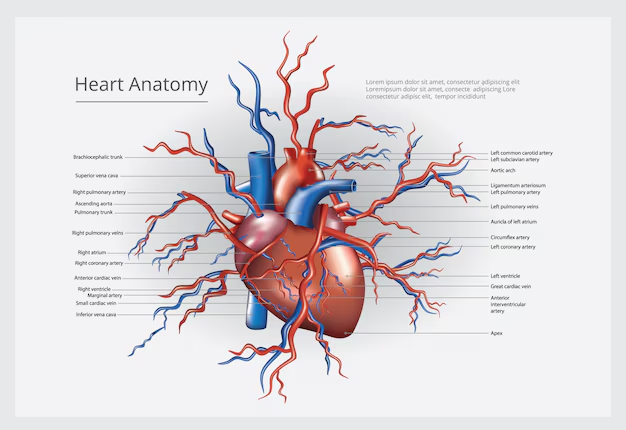
The aorta extends from the heart down to the abdomen, supplying blood to the upper body, arms, and legs. An aortic aneurysm occurs when a section of the aorta weakens and bulges, leading to potential complications. There are two main types of aortic aneurysms:
- Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm (TAA): Located in the section of the aorta that runs through the chest.
- Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA): Found in the section of the aorta that runs through the abdomen.
Symptoms
Often, aortic aneurysms develop silently and may not present symptoms until they reach a significant size or rupture. Common symptoms may include:
- Sudden, severe pain in the chest, back, or abdomen
- A pulsing sensation near the navel
- Shortness of breath
- Hoarseness or difficulty swallowing (especially in thoracic aneurysms)
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can contribute to the development of an aortic aneurysm:
- Atherosclerosis: Hardening of the arteries due to cholesterol buildup.
- Genetics: A family history of aneurysms increases risk.
- Hypertension: High blood pressure can weaken arterial walls.
- Age: The risk increases with age, particularly in men over 65.
- Smoking: Tobacco use is a significant risk factor.
Ayurvedic Perspective on Aortic Aneurysm
Ayurveda is a holistic healing system that emphasizes balance among the body, mind, and spirit. It categorizes individuals based on three primary doshas: Vata, Pitta, and Kapha. Each dosha has unique characteristics and influences health. Understanding an individual’s constitution can help tailor interventions to promote well-being.
Dosha Imbalances and Cardiovascular Health
In Ayurveda, aortic aneurysms may be viewed through the lens of dosha imbalances:
- Vata Imbalance: Associated with dryness, instability, and irregularities. Excess Vata may contribute to the weakening of tissues and arterial walls.
- Pitta Imbalance: Linked to heat and inflammation. Increased Pitta may lead to conditions that exacerbate cardiovascular issues.
- Kapha Imbalance: Characterized by heaviness and sluggishness. While Kapha is not directly linked to aneurysms, it can contribute to overall cardiovascular health if imbalanced.
Ayurvedic Principles for Managing Aortic Aneurysm
- Diet and Nutrition Ayurveda emphasizes the importance of a balanced diet tailored to one’s dosha. For individuals at risk of aortic aneurysm, the following dietary guidelines may be beneficial:
- Incorporate Heart-Healthy Foods: Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids (such as flaxseeds and walnuts), antioxidants (fruits and vegetables), and fiber (whole grains) can support cardiovascular health.
- Avoid Processed Foods: Minimize intake of refined sugars, unhealthy fats, and excessive salt, which can contribute to hypertension and atherosclerosis.
- Stay Hydrated: Adequate hydration supports overall vascular health.
- Herbal Remedies Ayurveda offers a range of herbs that may support cardiovascular health:
- Arjuna (Terminalia arjuna): Traditionally used for heart health, Arjuna may help strengthen heart muscles and improve circulation.
- Guggulu (Commiphora mukul): Known for its cholesterol-lowering properties, Guggulu may help reduce the risk of atherosclerosis.
- Turmeric (Curcuma longa): With its anti-inflammatory properties, turmeric can help reduce arterial inflammation.
- Lifestyle Modifications Implementing lifestyle changes is crucial in managing health:
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in moderate physical activity, such as walking, yoga, or swimming, can strengthen the cardiovascular system.
- Stress Management: Practices like meditation, pranayama (breathing exercises), and mindfulness can help reduce stress and promote emotional well-being.
- Adequate Sleep: Quality sleep is essential for overall health and recovery.
- Panchakarma Therapy Panchakarma is a detoxification and rejuvenation process in Ayurveda. It involves various therapies aimed at cleansing the body of toxins (ama) and restoring balance. For cardiovascular health, specific Panchakarma treatments may include:
- Abhyanga (Oil Massage): Promotes circulation and relaxation.
- Shirodhara: Involves pouring warm oil on the forehead, promoting mental clarity and reducing stress.
- Virechana: Therapeutic purgation to eliminate toxins from the body.
- Monitoring and Support Regular monitoring of cardiovascular health is vital. Ayurvedic practitioners can offer personalized guidance and support based on individual health status. Collaborative care with conventional healthcare providers is also essential for managing conditions like aortic aneurysms.
Conclusion
Understanding Aortic Aneurysm and Ayurvedic Approaches to Management pose serious health risks, necessitating comprehensive management approaches. While conventional medicine provides critical interventions, integrating Ayurvedic principles can enhance overall well-being and support cardiovascular health. By focusing on diet, lifestyle modifications, herbal remedies, and holistic therapies, individuals can cultivate balance and resilience.
As always, anyone experiencing symptoms or at risk of an aortic aneurysm should consult healthcare professionals for appropriate diagnosis and treatment. Ayurveda can be a valuable complement to conventional care, promoting a holistic approach to health and wellness.
Remember, maintaining a healthy lifestyle and addressing risk factors are key to preventing complications and supporting cardiovascular health in the long run.


Leave a reply