Ayurvedic Approaches to Tuberculosis: Integrating Ancient Wisdom with Modern Understanding
Ayurvedic Approaches to Tuberculosis: Integrating Ancient Wisdom with Modern Understanding is a chronic infectious disease primarily caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Characterized by a persistent cough, fever, night sweats, and weight loss, TB primarily affects the lungs but can spread to other parts of the body. While modern medicine has developed effective treatments for TB, including antibiotics and directly observed therapy (DOT), many individuals seek complementary approaches to enhance their overall well-being and support conventional treatment. One such approach is Ayurveda, an ancient system of medicine that originated in India over 3,000 years ago. This blog explores how Ayurvedic medicine addresses TB, aiming to harmonize traditional wisdom with contemporary medical practices.
Understanding Tuberculosis
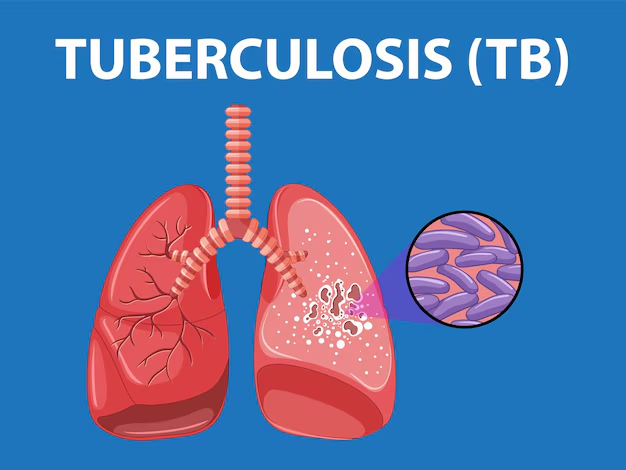
Before delving into Ayurveda, it’s essential to understand TB and its conventional management. TB is spread through airborne droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes. The body’s immune system responds to the bacteria, and in many cases, the infection remains latent, causing no symptoms. However, when the immune system is compromised, or if the bacteria are particularly virulent, the disease can become active, leading to significant health issues.
Modern TB treatment involves a combination of antibiotics, typically including isoniazid, rifampicin, ethambutol, and pyrazinamide. The treatment duration is usually six months or longer, depending on the TB strain and patient’s response. While these treatments are highly effective, they can come with side effects and require strict adherence, making supportive therapies like Ayurveda an appealing option for some patients.
Ayurvedic Perspective on Tuberculosis
Ayurveda, the “science of life,” emphasizes balance among the body’s three doshas (Vata, Pitta, and Kapha), which are believed to govern physiological and psychological functions. TB, in Ayurvedic terms, is viewed through the lens of imbalance in these doshas, particularly Kapha dosha, which governs the body’s fluids and mucus.
1. Dosha Imbalance and TB
In Ayurveda, TB is often associated with an imbalance in Kapha dosha, leading to excess mucus production and respiratory issues. The disease is described as a condition of Kshaya (emaciation) and Vata-Kapha disturbance. This means that the disease manifests with symptoms of wasting and an imbalance of mucus and air elements in the body.
Ayurvedic Treatment Strategies for Tuberculosis
Ayurvedic treatment for TB focuses on restoring balance to the doshas, boosting the immune system, and alleviating symptoms. It involves a combination of diet, herbal remedies, lifestyle changes, and detoxification procedures. Here’s a closer look at each component:
1. Diet
In Ayurveda, diet plays a crucial role in managing health conditions. For TB patients, a diet that helps strengthen the immune system and supports lung health is recommended.
- Warm, Nourishing Foods: Foods that are warm and easy to digest are preferred. This includes soups, stews, and cooked vegetables. Avoiding cold and raw foods helps prevent aggravation of Kapha dosha.
- High-Protein Foods: Since TB can lead to significant weight loss, incorporating high-protein foods such as legumes, nuts, seeds, and dairy products helps in muscle recovery and maintaining body strength.
- Spices and Herbs: Spices like turmeric, ginger, black pepper, and cumin are beneficial due to their anti-inflammatory and digestive properties. These spices help in reducing mucus and promoting overall well-being.
2. Herbal Remedies
Ayurveda utilizes a range of herbs that are believed to support lung health and boost immunity:
- Tulsi (Holy Basil): Known for its immune-boosting properties, Tulsi can help reduce inflammation and support respiratory function.
- Ashwagandha: This adaptogenic herb helps in managing stress and improving overall vitality, which is crucial for patients undergoing TB treatment.
- Giloy: Often used to enhance immunity and detoxify the body, Giloy is considered beneficial in combating infections and supporting recovery.
- Chyawanprash: A traditional Ayurvedic tonic, Chyawanprash is a combination of herbs and spices designed to rejuvenate the body, improve digestion, and strengthen the immune system.
3. Lifestyle and Detoxification
- Panchakarma: This detoxification therapy involves five key treatments designed to cleanse the body of toxins. Procedures like Vamana (therapeutic vomiting) and Virechana (purgation) are sometimes used to balance doshas and remove excess mucus.
- Pranayama and Yoga: Breathing exercises and yoga poses can help improve lung function, boost immunity, and reduce stress, which can be beneficial for TB patients.
- Adequate Rest: Ensuring sufficient rest and managing stress are vital for recovery. Ayurveda emphasizes the importance of a balanced lifestyle to support overall health.
4. Integrative Approach
While Ayurveda provides valuable insights and supportive therapies, it is crucial to integrate these practices with conventional TB treatment. Ayurvedic remedies should be used as complementary approaches rather than replacements for prescribed antibiotics. Consultation with both an Ayurvedic practitioner and a medical doctor ensures a comprehensive approach to managing TB.
Evidence and Research
Scientific research on Ayurvedic treatments for TB is limited compared to conventional medicine. However, some studies suggest that Ayurvedic herbs and practices can offer supportive benefits, such as enhancing immunity and reducing side effects associated with conventional treatments. For instance, Tulsi and Ashwagandha have been studied for their potential immune-enhancing properties.
Further research is needed to establish the efficacy and safety of Ayurvedic treatments for TB. Patients should always consult with healthcare providers to ensure that any complementary treatments are appropriate for their specific condition and do not interfere with conventional therapies.
Conclusion
Ayurveda, with its holistic approach, offers valuable insights and supportive treatments for managing tuberculosis. By addressing dosha imbalances, enhancing immunity, and incorporating lifestyle changes, Ayurveda aims to complement modern medical treatments and support overall well-being. However, it is essential for TB patients to adhere to prescribed medical treatments and consult with both conventional and Ayurvedic practitioners to ensure a safe and effective treatment plan.
Integrating Ayurvedic practices with conventional TB treatment can offer a balanced approach to managing this complex disease. As always, personalized care and a collaborative approach between different medical systems can provide the best outcomes for patients seeking comprehensive and holistic health solutions.


Leave a reply