Navigating Chronic Challenges: Approaches to Managing Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis
Navigating Chronic Challenges: Approaches to Managing Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis can be a complex and demanding journey. Both are forms of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that affect the digestive system, leading to symptoms that can significantly impact daily life. While there is no one-size-fits-all solution, a comprehensive approach to management can help alleviate symptoms, improve quality of life, and reduce the impact of these conditions.
Understanding Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis
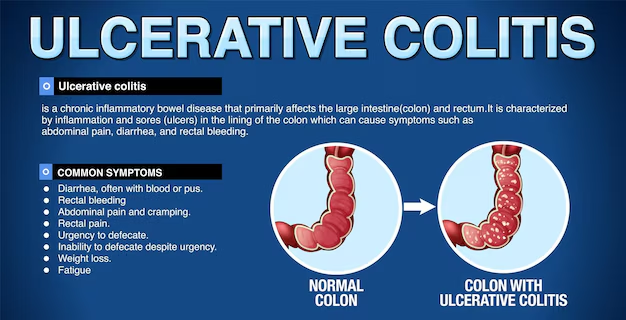
Navigating Chronic Challenges: Approaches to Managing Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis Before diving into management strategies, it’s important to understand what Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis entail. Both are characterized by inflammation in the digestive tract, but they differ in their specific manifestations.
- Crohn’s Disease: This condition can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract from the mouth to the anus. Inflammation can occur in patches, leaving healthy tissue between inflamed areas. Common symptoms include abdominal pain, diarrhea, weight loss, and fatigue.
- Ulcerative Colitis: This primarily affects the colon (large intestine) and rectum. Inflammation usually starts in the rectum and can spread continuously to the colon. Symptoms often include frequent, urgent bowel movements, rectal bleeding, and abdominal cramping.
Comprehensive Management Approaches
1. Medical Treatment
Medication is a cornerstone in managing both Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. The choice of medication depends on the severity of the condition, the specific areas affected, and the patient’s overall health.
- Anti-inflammatory Drugs: Medications such as 5-ASA (mesalamine) can help reduce inflammation in the intestines. These are often used for mild to moderate cases of ulcerative colitis.
- Corticosteroids: Prednisone and other corticosteroids are used to control inflammation during flare-ups. They are effective in the short term but are not suitable for long-term use due to potential side effects.
- Immunosuppressants: Drugs like azathioprine and mercaptopurine help suppress the immune system’s response to prevent inflammation. These are typically used for more severe cases or when other medications are not effective.
- Biologics: These newer drugs, such as infliximab and adalimumab, target specific molecules involved in the inflammatory process. They are often used when other treatments have failed.
- Antibiotics: In cases where infections or complications like abscesses occur, antibiotics may be necessary.
2. Dietary Management
Dietary adjustments can play a crucial role in managing symptoms and maintaining overall health.
- Identifying Trigger Foods: Some people with IBD find that certain foods exacerbate their symptoms. Common triggers include dairy products, high-fiber foods, and fatty foods. Keeping a food diary can help identify personal triggers.
- Low-FODMAP Diet: This diet involves reducing foods that are high in fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides, and polyols. It can help some individuals manage symptoms like bloating and gas.
- Balanced Nutrition: Ensuring adequate nutrient intake is vital, especially since malabsorption can be an issue. Working with a dietitian to create a balanced meal plan can help meet nutritional needs and manage symptoms.
- Hydration: Staying hydrated is important, particularly for those with diarrhea. Drinking plenty of fluids and considering electrolyte solutions can help prevent dehydration.
3. Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle changes can have a significant impact on managing IBD.
- Stress Management: Stress does not cause IBD but can exacerbate symptoms. Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and yoga can be helpful in managing stress.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular, moderate exercise can help improve overall well-being and manage symptoms. Activities such as walking, swimming, or cycling can be beneficial.
- Adequate Rest: Ensuring sufficient rest and managing fatigue is crucial. Balancing activity with rest can help maintain energy levels and overall health.
4. Psychological Support
Chronic conditions can take a toll on mental health, so addressing psychological well-being is essential.
- Counseling and Therapy: Speaking with a mental health professional can provide support for coping with the emotional aspects of living with IBD. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and other therapeutic approaches can be beneficial.
- Support Groups: Joining a support group for individuals with IBD can provide emotional support, practical advice, and a sense of community. Sharing experiences with others who understand the challenges can be empowering.
5. Surgical Options
For some individuals, surgery may be necessary when medication and other treatments are insufficient.
- Resection: In Crohn’s disease, surgery may involve removing affected sections of the intestines. This can help alleviate symptoms and address complications like strictures or fistulas.
- Colectomy: In severe cases of ulcerative colitis, removing the entire colon (colectomy) may be recommended. This can be performed with or without the creation of an ileostomy, depending on the patient’s situation.
- Proctocolectomy: This involves the removal of the colon and rectum, and may also include creating an ileal pouch (J-pouch) to allow for normal bowel function.
6. Monitoring and Ongoing Care
Regular monitoring and follow-up care are critical for managing Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
- Routine Check-ups: Regular visits with a gastroenterologist are essential for monitoring disease activity, adjusting treatment plans, and managing any complications.
- Laboratory Tests: Blood tests, stool tests, and imaging studies may be used to assess inflammation levels, nutrient deficiencies, and overall health.
- Flare-Up Management: Developing a plan for managing flare-ups, including recognizing early symptoms and knowing when to seek medical attention, can help minimize their impact.
Living Well with IBD
Navigating Chronic Challenges: Approaches to Managing Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis requires a multifaceted approach. By combining medical treatment, dietary management, lifestyle changes, psychological support, and ongoing care, individuals can better manage their condition and improve their quality of life.
It’s important to remember that each person’s experience with IBD is unique, and what works for one individual may not work for another. Collaborating with a healthcare team, including gastroenterologists, dietitians, and mental health professionals, can help tailor a management plan to individual needs and preferences.
Living with IBD is undoubtedly challenging, but with the right approach and support, it is possible to lead a fulfilling and active life. Whether through medication, dietary adjustments, lifestyle changes, or psychological support, finding the right balance is key to managing chronic inflammatory bowel disease effectively.


2 comments on “Navigating Chronic Challenges: Approaches to Managing Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis”
Dedicated Private Proxies Cheap
I went over this internet site and I believe you have a lot of superb info , saved to favorites (:.
Buy Fast Proxies
I really wanted to type a brief remark so as to express gratitude to you for all of the precious ideas you are posting at this site. My time intensive internet look up has finally been compensated with excellent content to write about with my great friends. I would express that we website visitors are truly lucky to dwell in a good site with so many wonderful professionals with insightful tactics. I feel pretty blessed to have seen the site and look forward to plenty of more awesome times reading here. Thanks a lot once more for a lot of things.