Controlling Blood Sugar Levels: Effective Strategies for Diabetes Management
Controlling Blood Sugar Levels Effective Strategies for Diabetes Management glucose is a critical component of our body’s energy supply. However, for individuals with diabetes, maintaining optimal blood sugar levels is a daily challenge. Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition that affects how the body metabolizes glucose, leading to elevated blood sugar levels that can cause serious health complications if not properly managed. Whether you have type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, or are at risk of developing diabetes, adopting effective strategies to control blood sugar levels is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being.
Understanding Blood Sugar and Diabetes
Blood sugar levels refer to the concentration of glucose present in the bloodstream at any given time. Glucose is derived from the foods we eat and serves as the primary source of energy for cells throughout the body. In healthy individuals, insulin—a hormone produced by the pancreas—helps regulate blood sugar levels by facilitating the uptake of glucose into cells for energy or storage.
In diabetes, however, there is either insufficient insulin production (as in type 1 diabetes) or the body’s cells become resistant to insulin’s effects (as in type 2 diabetes). As a result, glucose builds up in the bloodstream, leading to hyperglycemia (high blood sugar levels) which, if left untreated, can contribute to various complications such as cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, kidney problems, and vision impairment.
Effective Strategies for Controlling Blood Sugar Levels
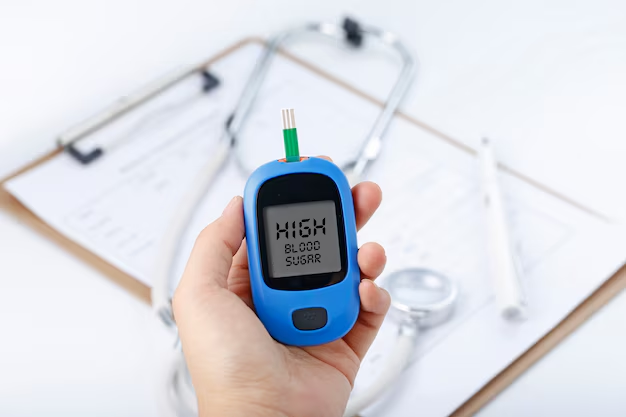
Managing diabetes involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, medication (if prescribed), and regular monitoring of blood sugar levels. Here are some effective strategies to help you keep your blood sugar levels within a healthy range:
1. Healthy Eating Habits
- Balanced Diet: Focus on consuming a variety of nutrient-dense foods including whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Avoid sugary beverages, refined carbohydrates, and excessive intake of saturated fats.
- Carbohydrate Counting: Monitor your carbohydrate intake as it directly affects blood sugar levels. Spread carbohydrates evenly throughout the day and pair them with protein and fiber to minimize blood sugar spikes.
- Glycemic Index Awareness: Choose foods with a lower glycemic index (GI), which release glucose more slowly into the bloodstream. Examples include whole grains, legumes, and non-starchy vegetables.
2. Regular Physical Activity
- Aerobic Exercise: Engage in moderate-intensity aerobic activities such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming for at least 150 minutes per week. Exercise helps your body use insulin more efficiently, lowering blood sugar levels.
- Strength Training: Incorporate resistance training exercises using weights or resistance bands to build muscle mass. Muscles play a key role in glucose metabolism, so strengthening them can improve blood sugar control.
3. Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
- Self-Monitoring: Regularly check your blood sugar levels using a glucose meter as recommended by your healthcare provider. This helps you understand how different foods, activities, and medications affect your blood sugar levels.
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM): For some individuals, CGM devices provide real-time information about glucose levels, helping to identify trends and make timely adjustments to diabetes management.
4. Medication and Insulin Therapy
- Oral Medications: If prescribed by your doctor, take oral medications as directed to help your body regulate blood sugar levels.
- Insulin Injections/Pump: For individuals with type 1 diabetes or advanced type 2 diabetes, insulin therapy may be necessary to maintain blood sugar control. Work closely with your healthcare team to determine the right insulin regimen for your needs.
5. Stress Management and Sleep
- Stress Reduction: Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, yoga, or tai chi to manage stress levels. Stress hormones can raise blood sugar levels, so finding healthy ways to cope is important.
- Quality Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of restful sleep each night. Poor sleep can disrupt hormone levels and contribute to insulin resistance, affecting blood sugar control.
Additional Tips for Diabetes Management
1. Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help flush out excess glucose and keep your body hydrated.
2. Regular Medical Check-ups: Schedule regular visits with your healthcare provider for diabetes screenings, blood tests, and overall health assessments.
3. Educational Resources and Support
- Diabetes Education: Attend diabetes education classes or workshops to learn more about managing your condition effectively.
- Support Groups: Join diabetes support groups or online communities to connect with others facing similar challenges and share experiences.
Controlling blood sugar levels is essential for managing diabetes and reducing the risk of complications. By adopting a proactive approach that includes healthy eating habits, regular physical activity, monitoring blood sugar levels, and adhering to prescribed medications, individuals with diabetes can achieve better overall health and quality of life. It’s important to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized diabetes management plan that meets your unique needs and goals. With dedication and consistency, maintaining optimal blood sugar levels is achievable, empowering you to live well with diabetes.



Leave a reply