Understanding Ankylosing Spondylitis: An Ayurvedic Perspective
Introduction
Understanding Ankylosing Spondylitis: An Ayurvedic Perspective is a chronic inflammatory disease primarily affecting the spine and the sacroiliac joints. It can lead to severe stiffness and pain, impacting a person’s quality of life. While conventional medicine often focuses on managing symptoms through anti-inflammatory medications and physical therapy, Ayurveda offers a holistic approach that addresses the root causes of the disease. In this blog, we’ll explore AS from an Ayurvedic perspective, including its causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
What is Ankylosing Spondylitis?
AS is a type of arthritis that primarily affects the axial skeleton. It is characterized by inflammation of the spine, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. Over time, this can result in fusion of the vertebrae, a condition known as ankylosis, which can severely limit spinal flexibility.
Symptoms of Ankylosing Spondylitis
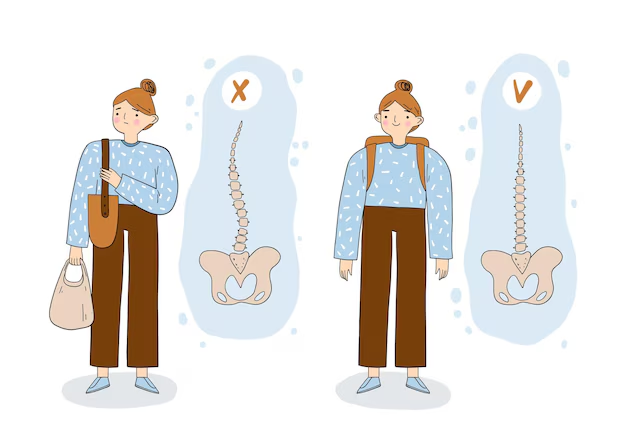
- Chronic Pain: Persistent pain in the lower back and buttocks.
- Stiffness: Particularly noticeable in the morning or after periods of inactivity.
- Fatigue: General tiredness is common in chronic inflammatory diseases.
- Postural Changes: Over time, individuals may develop a stooped posture due to spinal fusion.
- Eye Inflammation: Conditions like uveitis can occur in some individuals.
Causes of Ankylosing Spondylitis
While the exact cause of AS is unknown, it is believed to have a genetic component, with a strong association with the HLA-B27 antigen. Factors contributing to the disease may include:
- Genetics: Family history plays a significant role.
- Environmental Triggers: Infections or trauma may trigger the onset in genetically predisposed individuals.
Ayurveda: An Overview
Ayurveda, an ancient Indian system of medicine, focuses on balancing the body’s energies, or doshas—Vata, Pitta, and Kapha. It emphasizes a holistic approach to health, addressing the physical, emotional, and spiritual aspects of well-being. In Ayurveda, diseases like AS are viewed as imbalances in the body’s doshas and dhatus (tissues).
Ayurvedic View on Ankylosing Spondylitis
In Ayurveda, AS is often correlated with the aggravation of Vata dosha, which governs movement and flexibility in the body. The disease may also involve imbalances in Pitta, particularly in cases where inflammation is prominent. The Ayurvedic understanding of AS encompasses:
- Imbalance of Doshas: Vata aggravation can lead to stiffness and pain, while Pitta can contribute to inflammation.
- Ama Formation: The presence of toxins (ama) in the body due to improper digestion or lifestyle choices is believed to play a significant role in chronic diseases, including AS.
Ayurvedic Treatment Approaches for Ankylosing Spondylitis
Ayurveda employs a multifaceted approach to treat AS, aiming to restore balance to the doshas and eliminate toxins. Here are some key treatment modalities:
1. Dietary Modifications
Diet plays a crucial role in Ayurveda. A balanced diet can help manage inflammation and support overall health.
- Anti-inflammatory Foods: Include turmeric, ginger, and garlic, which are known for their anti-inflammatory properties.
- Warm Foods: Opt for cooked foods rather than raw, as warm foods are easier to digest and can help reduce Vata aggravation.
- Avoid Heavy Foods: Minimize intake of red meat, dairy, and processed foods that can lead to ama formation.
2. Herbal Remedies
Several herbs are beneficial in managing symptoms of AS:
- Guggulu (Commiphora mukul): Known for its anti-inflammatory properties, it can help reduce pain and stiffness.
- Turmeric (Curcuma longa): Contains curcumin, which has powerful anti-inflammatory effects.
- Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera): An adaptogen that can help manage stress and inflammation.
3. Panchakarma Therapy
Panchakarma is a detoxification process that aims to eliminate ama from the body. It includes:
- Abhyanga (Oil Massage): A warm oil massage can help alleviate pain and improve circulation.
- Swedana (Steam Therapy): Promotes sweating and helps in detoxifying the body.
- Basti (Enema Therapy): This can be particularly effective in balancing Vata and reducing pain in the lower back.
4. Yoga and Physical Activity
Yoga is an integral part of Ayurvedic treatment, focusing on gentle stretching and strengthening exercises that enhance flexibility and reduce stiffness.
- Gentle Asanas: Poses like Bhujangasana (Cobra Pose) and Marjaryasana (Cat-Cow Stretch) can help maintain spinal mobility.
- Pranayama (Breathing Exercises): Practices like Anulom Vilom can help reduce stress and improve lung capacity.
5. Lifestyle Modifications
Incorporating healthy lifestyle habits is essential in managing AS:
- Regular Routine: Maintain a consistent daily routine to balance Vata.
- Stress Management: Practice meditation and mindfulness to manage stress levels, as stress can exacerbate symptoms.
Conclusion
Ankylosing Spondylitis can significantly impact the quality of life, but Ayurveda offers a holistic approach to management. By addressing the root causes of the disease and focusing on dietary changes, herbal remedies, detoxification, yoga, and lifestyle modifications, individuals can find relief and improve their overall well-being.
It’s essential to consult with a qualified Ayurvedic practitioner for personalized treatment plans. By integrating Ayurvedic principles with conventional treatment, patients can embark on a path toward better health and improved quality of life.
As always, maintain open communication with healthcare providers and remain informed about the latest research and treatment options for Ankylosing Spondylitis.



Leave a reply