Understanding Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) and Ayurvedic Approaches to Management
Introduction
Understanding Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) and Ayurvedic Approaches to Management is a common digestive disorder characterized by the backward flow of stomach acids into the esophagus. This condition often leads to symptoms such as heartburn, regurgitation, and discomfort in the chest. While conventional medicine typically employs antacids, proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), and lifestyle modifications to manage GERD, Ayurveda offers a holistic approach that emphasizes balancing the body’s energies and treating the root cause of the disease. This blog delves into GERD from an Ayurvedic perspective, exploring how traditional remedies and lifestyle changes can offer relief and potentially restore balance.
Understanding GERD
GERD occurs when the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), a ring of muscle between the esophagus and stomach, becomes weakened or relaxed, allowing stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus. This acid reflux can cause irritation and inflammation in the esophageal lining, leading to the symptoms commonly associated with GERD.
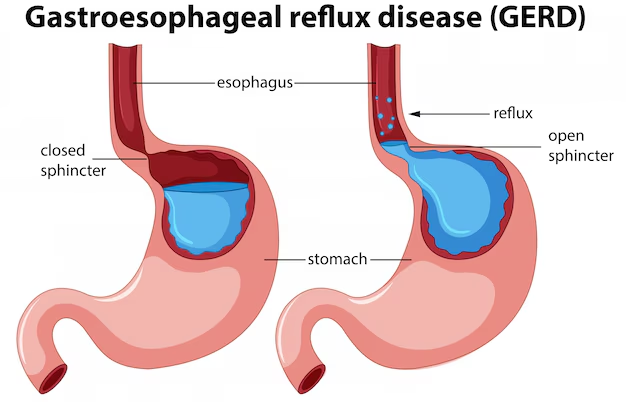
Common Symptoms
- Heartburn: A burning sensation in the chest or throat.
- Regurgitation: The sensation of acid backing up into the throat or mouth.
- Dysphagia: Difficulty swallowing.
- Chest Pain: Discomfort or pain in the chest area.
- Chronic Cough: Persistent coughing or throat clearing.
Conventional Management
Conventional treatments for GERD include lifestyle modifications, medications like PPIs and H2-receptor antagonists, and in severe cases, surgical interventions. While these methods can offer symptom relief, they often do not address the underlying imbalances that contribute to the disorder.
Ayurvedic Perspective on GERD
Ayurveda, the ancient system of medicine from India, views GERD through the lens of three fundamental energies or doshas: Vata, Pitta, and Kapha. According to Ayurveda, GERD is primarily related to an imbalance in the Pitta dosha, which governs digestion, metabolism, and transformation in the body. An aggravated Pitta can lead to excess acid production and a weakened digestive fire (Agni), resulting in GERD symptoms.
Pitta Dosha and GERD
- Pitta Imbalance: Excess Pitta can increase acid production in the stomach, leading to the symptoms of GERD. Factors such as stress, spicy foods, and improper eating habits can exacerbate Pitta imbalance.
- Digestive Fire (Agni): In Ayurveda, a strong digestive fire is crucial for proper digestion. When Agni is impaired, it can result in poor digestion and acid reflux.
Ayurvedic Management of GERD
Ayurvedic management of GERD focuses on balancing the Pitta dosha, restoring digestive fire, and promoting overall digestive health. The approach includes dietary modifications, herbal remedies, and lifestyle changes.
1. Dietary Modifications
Diet plays a crucial role in managing GERD in Ayurveda. The goal is to avoid foods that aggravate Pitta and promote foods that soothe and balance the digestive system.
- Avoid Pitta-Aggravating Foods: Spicy, acidic, and overly salty foods can exacerbate GERD symptoms. These include chili peppers, tomatoes, and citrus fruits.
- Incorporate Pitta-Pacifying Foods: Opt for cooling and soothing foods such as cucumber, mint, and coconut. Sweet fruits like apples and pears are also beneficial.
- Eat Small, Frequent Meals: Large meals can increase acid production. Eating smaller, more frequent meals can help manage GERD symptoms.
- Include Bitter and Astringent Foods: Foods with bitter and astringent tastes, such as leafy greens and pomegranate, can help balance Pitta and reduce acid reflux.
2. Herbal Remedies
Ayurvedic herbs are used to balance Pitta, strengthen digestive fire, and soothe the digestive tract. Here are some commonly used herbs for GERD:
- Amla (Indian Gooseberry): Known for its cooling properties, Amla helps balance Pitta and supports digestive health. It can be taken in the form of powder or as a supplement.
- Licorice Root (Yashtimadhu): Licorice root has soothing and anti-inflammatory properties that can help heal the esophageal lining and reduce acid reflux.
- Triphala: This herbal blend of three fruits (Amla, Haritaki, and Bibhitaki) supports digestion, promotes regular bowel movements, and helps balance Pitta.
- Chamomile: Chamomile tea can soothe the digestive tract and reduce inflammation associated with GERD.
3. Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle modifications are an integral part of Ayurvedic treatment for GERD. These changes focus on reducing stress, improving digestion, and promoting overall well-being.
- Manage Stress: Stress can exacerbate GERD symptoms by increasing acid production. Techniques such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises can help manage stress and balance Pitta.
- Follow a Consistent Eating Schedule: Regular meal times and avoiding late-night eating can help improve digestion and reduce GERD symptoms.
- Practice Proper Eating Habits: Eat slowly, chew food thoroughly, and avoid overeating. These habits support better digestion and reduce acid reflux.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to support digestion and prevent dehydration.
Conclusion
Understanding Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) and Ayurvedic Approaches to Management can be a challenging condition, but Ayurvedic medicine offers a holistic approach to managing and potentially alleviating the symptoms. By focusing on balancing the Pitta dosha, restoring digestive fire, and making mindful dietary and lifestyle changes, Ayurveda provides a comprehensive strategy for addressing GERD. Integrating Ayurvedic principles with conventional treatments can offer a balanced path to better digestive health and overall well-being.
As with any medical condition, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new treatment regimen. Combining the wisdom of Ayurveda with modern medical advice can help you find the most effective approach to managing GERD and improving your quality of life.


Leave a reply