The Journey of Organic Food: From Farm to Table
In an era where health consciousness is at an all-time high, the demand for Organic Food has surged. More and more people are making a deliberate choice to eat organic, driven by a desire for healthier options and a more sustainable planet. But have you ever wondered what goes into bringing that fresh, organic produce to your table? This blog delves into the fascinating journey of Organic Food, from the farm to your table, and why this journey is worth every bit of effort.
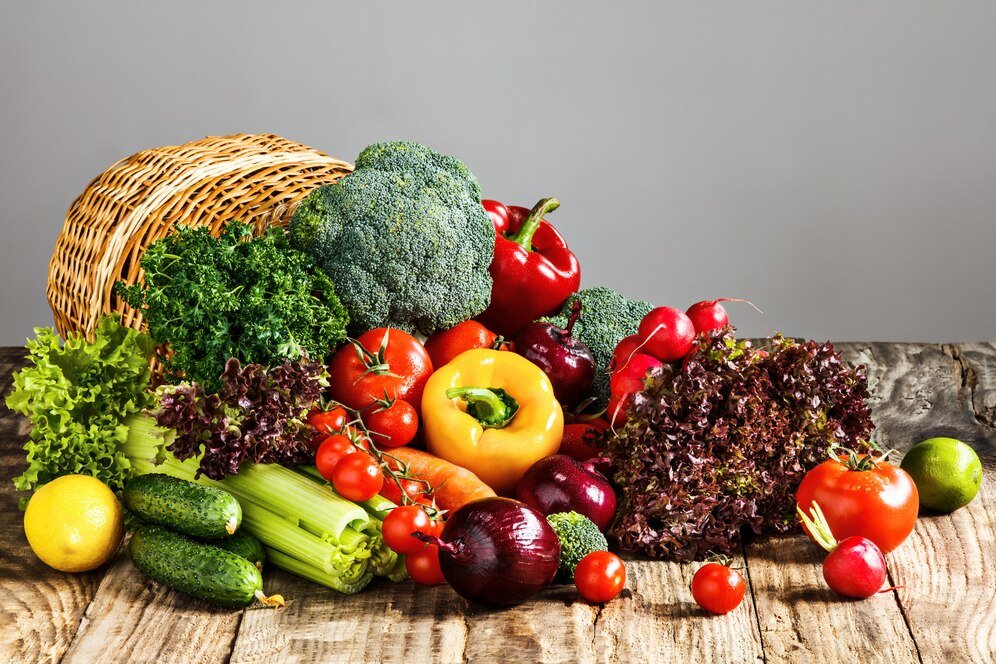
What Is Organic Food?
Before we embark on the journey, it’s essential to understand what qualifies as Organic Food. Organic Food is grown without the use of synthetic pesticides, genetically modified organisms (GMOs), fertilizers, or other artificial additives. Instead, organic farming relies on natural processes and biodiversity to maintain soil health and produce nutritious crops.
Why Choose Organic?
The reasons for choosing Organic Food are manifold:
- Health Benefits: Organic Foods are free from harmful chemicals and are richer in nutrients.
- Environmental Sustainability: Organic farming practices promote biodiversity and reduce pollution.
- Animal Welfare: Organic standards ensure that animals are treated humanely.
- Taste and Quality: Many people find that Organic Food tastes better and is fresher.

By Khet Se Ghar
Now, let’s explore the journey of Organic Food from the farm to your table.
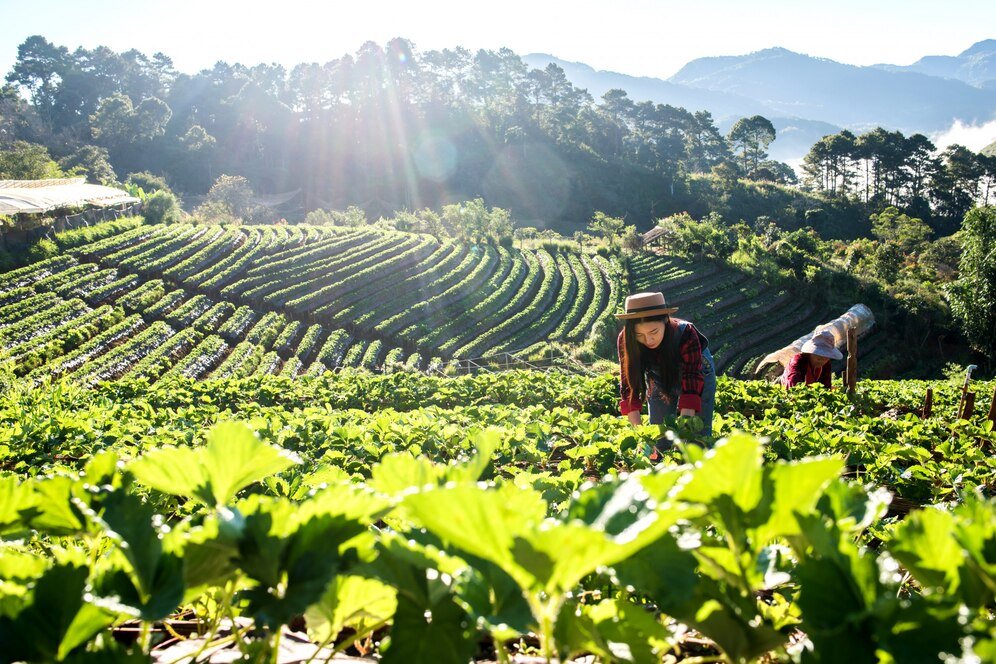
Step 1: The Organic Farm
Soil Preparation
The journey begins with the soil. Organic farming places a strong emphasis on soil health. Farmers use natural compost, green manure, and organic fertilizers to enrich the soil. Crop rotation and cover cropping are also common practices that help maintain soil fertility and structure.
Planting
Once the soil is ready, it’s time for planting. Organic farmers choose seeds that are non-GMO and often heirloom varieties, which are known for their resilience and nutritional value. These seeds are planted in nutrient-rich soil, where they can grow strong and healthy.
Natural Pest Control
One of the key challenges in farming is pest control. Organic farmers use natural methods such as introducing beneficial insects like ladybugs and predatory beetles to control pests. Additionally, they employ crop rotation and intercropping to disrupt the life cycles of pests and diseases.
Water Management
Water is a precious resource, and organic farming employs efficient water management practices. Techniques such as drip irrigation and rainwater harvesting are used to conserve water and ensure that crops receive the right amount of moisture.

By Khet Se Ghar
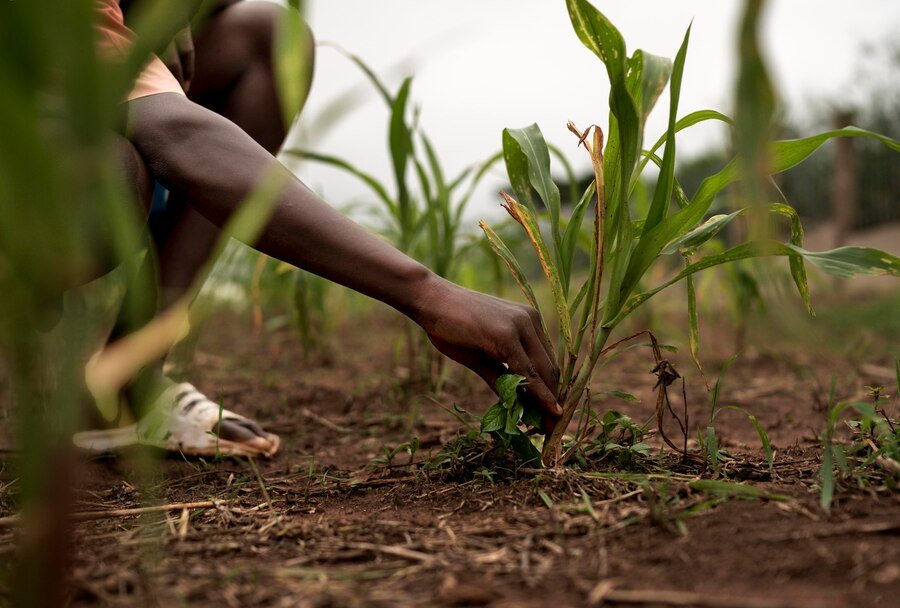
Step 2: Harvesting
Timing
Timing is crucial when it comes to harvesting organic produce. Farmers carefully monitor their crops to determine the optimal time for harvest, ensuring that the fruits and vegetables are at their peak in terms of flavor and nutritional value.
Manual Harvesting
Organic farming often involves more manual labor than conventional farming. Crops are usually harvested by hand to minimize damage and maintain quality. This method allows farmers to select only the best produce for the next steps in the journey.
Post-Harvest Handling
After harvesting, the produce undergoes careful handling to prevent bruising and spoilage. Organic farmers often use biodegradable packaging materials to reduce environmental impact. The produce is then quickly transported to storage facilities to maintain freshness.

By Khet Se Ghar
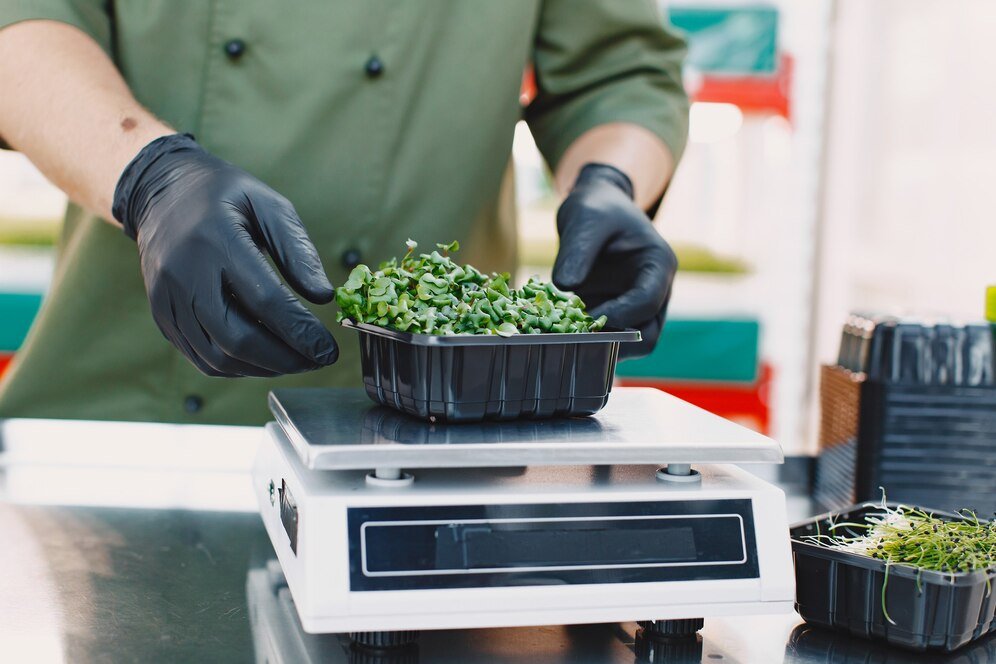
Step 3: Processing and Packaging
Minimal Processing
One of the hallmarks of organic food is minimal processing. Unlike conventional foods, which often undergo extensive processing, Organic Food are typically processed in ways that preserve their natural state. This means fewer additives and preservatives.
Certification and Labeling
Before organic products can reach the market, they must undergo certification by recognized authorities. This certification process ensures that the food meets strict organic standards. Certified organic products carry labels that help consumers make informed choices.
Sustainable Packaging
Packaging plays a significant role in the journey of organic food. Many organic producers opt for eco-friendly packaging materials that are biodegradable or recyclable. This reduces the environmental footprint of Organic Food and aligns with the principles of sustainability.

By Khet Se Ghar
Step 4: Distribution
Local Distribution
One of the advantages of Organic Food is that it often involves shorter supply chains. Many organic farms distribute their produce locally through farmers’ markets, community-supported agriculture (CSA) programs, and local grocery stores. This not only supports local economies but also reduces the carbon footprint associated with transportation.
Online and Retail Distribution
In addition to local distribution, Organic Food is also available through online platforms and retail stores. Many consumers appreciate the convenience of ordering organic products online and having them delivered to their doorsteps. Retail stores often feature dedicated sections for Organic Food , making it easier for consumers to find and purchase organic options.
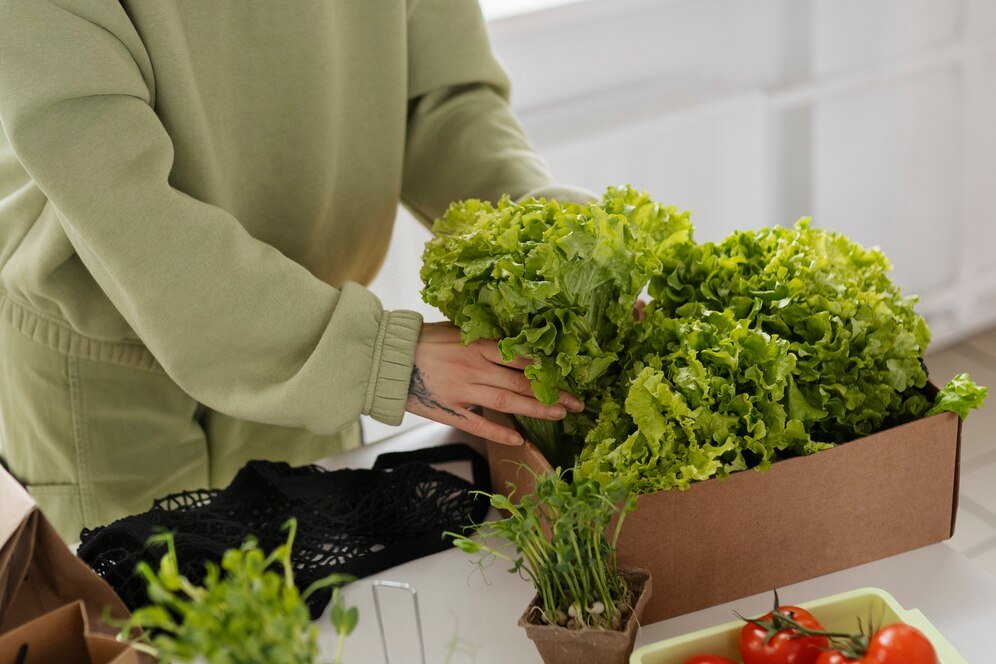

By Khet Se Ghar
Step 5: From Store to Table
Buying Organic
When buying organic food, it’s important to look for certification labels such as USDA Organic, EU Organic, or other recognized standards. These labels guarantee that the product has been grown and processed according to strict organic guidelines.
Storing Organic Produce
Proper storage is essential to maintain the freshness and quality of organic produce. Store fruits and vegetables in the refrigerator and use breathable bags or containers to prevent moisture buildup. Root vegetables like potatoes and onions should be kept in a cool, dark place.
Cooking and Enjoying
Finally, the journey culminates in your kitchen. Organic Food can be prepared in countless delicious ways. Whether you’re making a simple salad with fresh organic greens or cooking a hearty stew with organic vegetables, you’re sure to enjoy the rich flavors and nutritional benefits.

By Khet Se Ghar
The Benefits of Organic Food
Health Benefits
Organic Food is often richer in essential nutrients, such as vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. By avoiding synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, organic farming also reduces your exposure to harmful chemicals, which can have long-term health implications.
Environmental Benefits
Organic farming practices are designed to work with nature rather than against it. By promoting soil health, reducing pollution, and encouraging biodiversity, organic farming helps to protect our environment for future generations.
Economic Benefits
Supporting organic farming can also have economic benefits. By purchasing organic products, you help support small-scale farmers and contribute to local economies. Additionally, organic farming practices often require more labor, which can create jobs and support rural communities.
Overcoming Challenges
While the benefits of Organic Food are clear, it’s important to acknowledge the challenges. Organic farming can be labor-intensive and often yields less produce compared to conventional farming. This can result in higher prices for consumers. However, many people find that the benefits of Organic Food far outweigh the costs.
Conclusion
The journey of Organic Food from farm to table is a testament to the dedication and hard work of organic farmers who prioritize health, sustainability, and quality. By choosing organic food, you are not only making a healthier choice for yourself but also supporting practices that benefit the environment and society as a whole.
As awareness about the importance of Organic Food continues to grow, it’s clear that this movement is more than just a trend—it’s a fundamental shift towards a more sustainable and health-conscious way of living. The next time you enjoy a fresh, organic meal, take a moment to appreciate the journey that brought it to your table. It’s a journey worth every step, for the betterment of our health and the planet.
Embrace the organic lifestyle, and enjoy the journey of food that truly nourishes your body and soul.




Leave a reply