Navigating Diabetes: Essential Precautions for Patients
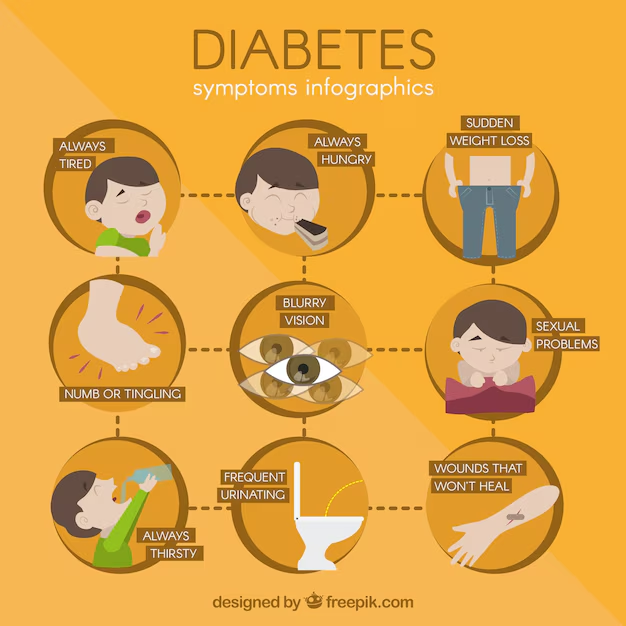
Navigating Diabetes: Essential Precautions for Patients is a chronic health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the body either cannot produce enough insulin or cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps regulate blood sugar levels and allows cells to use glucose for energy.
There are two main types of diabetes: type 1 and type 2.
- Type 1 Diabetes:Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition in which the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. As a result, the body produces little to no insulin. Type 1 diabetes is usually diagnosed in children and young adults, although it can occur at any age. People with type 1 diabetes require lifelong insulin therapy to manage their blood sugar levels.
- Type 2 Diabetes:Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes, accounting for around 90% of all cases. It occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or does not produce enough insulin to meet its needs. Type 2 diabetes is often associated with lifestyle factors such as obesity, physical inactivity, and poor diet.

Living with diabetes demands careful attention to various aspects of daily life to manage the condition effectively and maintain overall health. For individuals diagnosed with diabetes, whether type 1 or type 2, adopting specific precautions becomes imperative to prevent complications and ensure a good quality of life. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into crucial precautions that diabetes patients should integrate into their routines.
- Dietary Considerations: Transitioning to a diabetes-friendly diet is paramount. Focus on consuming foods with a low glycemic index, such as whole grains, vegetables, fruits, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Avoid sugary beverages, refined carbohydrates, and processed foods. Regular meal timings and portion control are essential to manage blood sugar levels effectively.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in physical activity is crucial for diabetes management. Regular exercise helps lower blood sugar levels, improves insulin sensitivity, and promotes weight management. Incorporate a mix of aerobic exercises, strength training, and flexibility exercises into your routine. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, spread across several days.
- Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels:Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is vital for diabetes management. Keep track of your levels as advised by your healthcare provider. This helps in understanding how your body responds to various foods, activities, and medications, enabling better management of the condition.
- Medication Adherence: Adhering to prescribed medication regimens is essential for diabetes management. Take medications as directed by your healthcare provider, and never skip doses. Ensure you understand the purpose and potential side effects of each medication. Report any adverse effects promptly to your healthcare team.
- Foot Care: Diabetes can affect circulation and nerve function in the feet, increasing the risk of foot complications. Inspect your feet daily for any cuts, blisters, or sores, and promptly treat any injuries. Wear comfortable, well-fitting shoes and avoid walking barefoot. Regularly visit a podiatrist for foot exams.
- Eye Care: Diabetes increases the risk of eye complications such as diabetic retinopathy and glaucoma. Attend regular eye examinations to detect any issues early and prevent vision loss. Maintain optimal blood sugar levels to reduce the risk of diabetic eye disease.
- Dental Health: Diabetes is associated with an increased risk of gum disease and dental issues. Practice good oral hygiene by brushing and flossing your teeth regularly. Visit your dentist for routine check-ups and cleanings. Inform your dentist about your diabetes status.
- Stress Management: Stress can affect blood sugar levels and overall well-being. Practice stress-reducing techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, yoga, or engaging in hobbies you enjoy. Ensure an adequate amount of sleep each night to support stress management and overall health.
- Hydration: Stay adequately hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day. Dehydration can affect blood sugar levels and lead to other health complications. Limit the consumption of sugary drinks and opt for water or unsweetened beverages instead.
- Regular Medical Check-ups: Regular medical check-ups are essential for diabetes management. Schedule appointments with your healthcare provider for comprehensive assessments of your diabetes control, blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and overall health. Discuss any concerns or changes in your condition during these visits.
- Emergency Preparedness:Be prepared for emergencies by keeping essential supplies such as glucose tablets or gel, a glucagon kit (if prescribed), and medical identification handy. Educate family members or close contacts about what to do in case of a diabetes-related emergency.
- Community Support: Joining diabetes support groups or communities can provide valuable emotional support, practical tips, and insights from others living with diabetes. Share experiences, learn from others, and find encouragement in knowing that you’re not alone in your journey.
Conclusion
Navigating Diabetes: Essential Precautions for Patients, navigating life with diabetes requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses dietary modifications, regular exercise, medication adherence, and various other precautions. By incorporating these essential precautions into their daily routines, individuals with diabetes can effectively manage their condition, reduce the risk of complications, and enjoy a better quality of life. Remember, proactive management and self-care are key to thriving with diabetes.



Leave a reply